The laws of supply and demand are foundation economic principles that is the primary motivation for producers and consumers in making their decisions.
The law of demand says the higher the price of a product the less customers will want of a product or service. Demand is set from the law of diminishing value versus price, consumers prioritize essential needs first and purchase additional items with disposable income left over. As prices rise demand for a good or service decline based on its marginal utility.
The market demand curve chart shows the quantity of demand for different tiers of pricing for total available customers.
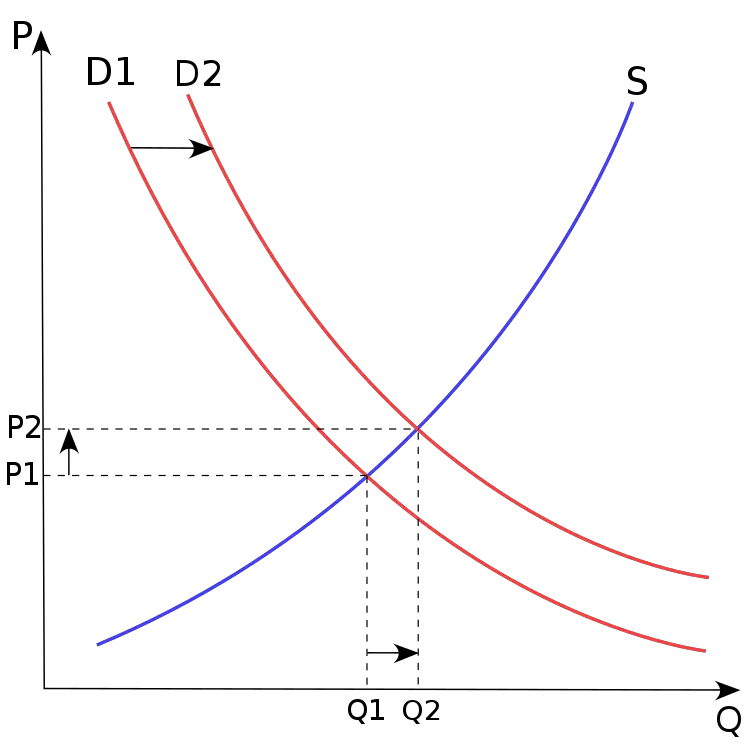
Current demand shifts in magnitude due to trends and changes in popularity, preferences, income, necessity, or competition from technology or copy cats not always from increase in price alone.
The law of supply says that when other factors are kept constant then an increase in prices causes an increase in the quantity created for the market place. Price and quantity available are directly related and create motivation for supply and demand through reward for producing and ability to acquire. The quantities available respond in the direction of price action for goods and services. Creators and producers are motivated to create and sell a larger quantity of a product to the market for higher prices by growing production capacity to increase profits.
The law of supply is the correlation between quantity that is supplied into the market place and the set price of goods and services and is why their is an upward slope in a supply curve.
The law of supply and demand in the market tries to create an equilibrium between the producers and suppliers of goods and services and the consumers of goods and services. In a free market prices should settle into an efficient level that motivates producers to bring the goods to the market and the consumer is willing to pay to possess the goods. Prices should rise on increased demand or scarcity and prices should fall on decreased demand or over supply.
Prices should meet where supply and demand finds a buyer and a seller that agree on a transaction.
This is how the free market is supposed to work based on the law of economics.